Even or odd using ternary (conditional) operator
C program to determine whether the number entered by user is even or odd using conditional operator.
Program
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int num;
printf("Enter a number\t: ");
scanf("%d",&num);
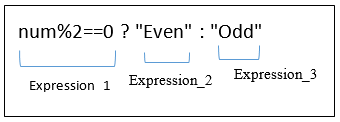
num%2 == 0 ? printf("Even number") : printf("Odd number");
getch();
}
Output
********** Run1 **********
Enter a number : 8
Even number
********** Run2 **********
Enter a number : 5
Odd number
Explanation
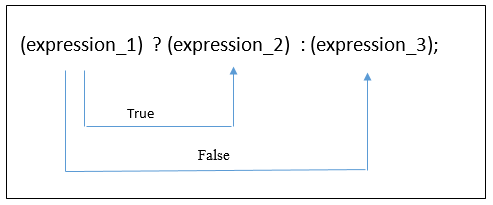
General Form of Ternary Operator (conditional operator):
expression_1 is a comparison/conditional argument. If expression_1 results in true then, expression_2 is executed/returned, and if expression_1 results in false then, expression_3 gets executed/returned.
In above program, we check if the user entered number (num) is perfectly divisible by 2 or not. If its perfectly divisible by 2, then it is an even number or else it is an odd number.
Using conditional operator, this is done as follows:

If num%2==0 evaluates to true, then
If num%2==0 evaluates to false, then
(expression_1) ? (expression_2) : (expression_3);
expression_1 is a comparison/conditional argument. If expression_1 results in true then, expression_2 is executed/returned, and if expression_1 results in false then, expression_3 gets executed/returned.

In above program, we check if the user entered number (num) is perfectly divisible by 2 or not. If its perfectly divisible by 2, then it is an even number or else it is an odd number.
Using conditional operator, this is done as follows:
num%2 == 0 ? printf("Even number") : printf("Odd number");

If num%2==0 evaluates to true, then
printf("Even number"); statement is executed.
If num%2==0 evaluates to false, then
printf("Odd number"); statement is executed.
Program
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int num;
printf("Enter a number\t: ");
scanf("%d",&num);
printf("The number is %s",(num%2==0 ? "Even" : "Odd"));
getch();
}
Output
********** Run1 **********
Enter a number : 12
The number is Even
********** Run2 **********
Enter a number : 11
The number is Odd
Explanation
General Form of Ternary Operator (conditional operator):
expression_1 is a comparison/conditional argument. If expression_1 results in true then, expression_2 is executed/returned, and if expression_1 results in false then, expression_3 gets executed/returned.

In above program, we check if the user entered number (num) is perfectly divisible by 2 or not. If its perfectly divisible by 2, then it is an even number or else it is an odd number.
Using conditional operator, this is done as follows:
Here, conditional operator is used as an argument in printf() statement.
If num%2==0 evaluates to true, then "Even" statement is returned and printf() statement becomes
If num%2==0 evaluates to false, then "Odd" statement is returned and printf() statement becomes
(expression_1) ? (expression_2) : (expression_3);
expression_1 is a comparison/conditional argument. If expression_1 results in true then, expression_2 is executed/returned, and if expression_1 results in false then, expression_3 gets executed/returned.

In above program, we check if the user entered number (num) is perfectly divisible by 2 or not. If its perfectly divisible by 2, then it is an even number or else it is an odd number.
Using conditional operator, this is done as follows:
printf("The number is %s",(num%2==0 ? "Even" : "Odd"));

Here, conditional operator is used as an argument in printf() statement.
If num%2==0 evaluates to true, then "Even" statement is returned and printf() statement becomes
printf("The number is %s","Even");
If num%2==0 evaluates to false, then "Odd" statement is returned and printf() statement becomes
printf("The number is %s","Odd");